 Can AI Auto Accessories Revolutionize Modern Vehicle Convenience and Safety?
Can AI Auto Accessories Revolutionize Modern Vehicle Convenience and Safety?

Jan 30, 2026
AI auto accessories represent a significant leap in vehicle technology, combining artificial intelligence with everyday car enhancements. These smart devices are designed to improve safety, streamline operations, and provide drivers with advanced convenience features. From adaptive cruise controls to AI-powered parking assistants, these innovations are transforming how we interact with vehicles.
As cars become more connected, AI auto accessories help integrate data from sensors, cameras, and onboard systems to optimize performance, reduce human error, and create a seamless driving experience. The adoption of these technologies is no longer limited to luxury vehicles; even standard models can now benefit from AI enhancements.
One of the primary advantages of AI auto accessories is their ability to enhance vehicle safety. AI-driven systems can detect potential hazards faster than human reflexes, alerting drivers to obstacles, pedestrians, or sudden changes in traffic conditions. Features such as lane-keeping assist, automatic emergency braking, and collision avoidance rely heavily on AI algorithms to ensure timely intervention.
These AI systems not only respond to immediate threats but also learn from driving patterns and environmental conditions. Over time, this continuous learning improves predictive capabilities, enabling vehicles to anticipate risks and optimize driving behavior.
AI auto accessories simplify everyday driving tasks, reducing cognitive load and improving user experience. Voice-activated controls, AI navigation systems, and predictive maintenance alerts allow drivers to focus on the road while enjoying enhanced comfort and connectivity.
Integration with mobile apps and cloud platforms allows seamless monitoring of vehicle health, scheduling maintenance, and even remote control of certain functions. These systems empower drivers to manage their vehicles efficiently and anticipate needs before issues arise.
AI auto accessories contribute to enhanced vehicle efficiency by optimizing energy use, engine performance, and driving patterns. Intelligent systems can adjust acceleration, braking, and power distribution based on traffic conditions and driver behavior, reducing fuel consumption and wear on vehicle components.
Fleet operators and individual drivers alike benefit from AI monitoring that tracks efficiency metrics, identifies inefficient driving habits, and provides actionable insights. Over time, these adjustments lead to measurable improvements in both cost savings and environmental impact.
Despite their benefits, AI auto accessories require careful consideration. Integration with vehicle electronics, software updates, and cybersecurity risks are important factors for consumers and manufacturers. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems and regulatory compliance is essential for safe adoption.
Furthermore, user education is crucial. Drivers must understand the capabilities and limitations of AI accessories to avoid overreliance. Balancing automation with human oversight ensures maximum safety and efficiency.
The future of AI auto accessories is promising, with advancements in machine learning, sensor technology, and connectivity. As vehicles become smarter, AI-driven enhancements will continue to expand, enabling autonomous features, predictive analytics, and fully integrated smart vehicle ecosystems.
Consumers can expect more personalized driving experiences, improved safety protocols, and increased vehicle longevity. Early adoption of AI auto accessories positions both manufacturers and drivers at the forefront of modern automotive innovation.
AI auto accessories are transforming the automotive landscape by enhancing safety, convenience, and performance. Their integration empowers drivers, reduces risk, and delivers smarter, more efficient vehicles. Investing in AI-driven technologies ensures vehicles remain modern, responsive, and aligned with the evolving demands of mobility.
By embracing AI auto accessories, drivers can experience a new level of comfort and security while manufacturers benefit from innovative features that drive industry progress. This combination of safety, convenience, and intelligence marks a turning point in automotive technology.

 How Do Kinfor Truck Accessories Meet the Demands of Long-Haul Trucking?
How Do Kinfor Truck Accessories Meet the Demands of Long-Haul Trucking?

Jan 23, 2026
Long-haul trucking presents unique challenges, from extended driving hours to demanding road conditions and tight delivery schedules. Truck operators and fleet managers increasingly rely on high-quality accessories to enhance vehicle performance, safety, and driver comfort. Kinfor truck accessories have emerged as a trusted solution, offering a wide range of products designed specifically for the needs of long-haul drivers and commercial fleets.
By integrating innovative features into trucks, Kinfor accessories help reduce driver fatigue, prevent maintenance issues, and improve overall operational efficiency. Their focus on durable materials and practical design ensures that accessories perform reliably under the stresses of daily long-distance driving.
Driver comfort is a critical factor in long-haul trucking. Extended periods behind the wheel can lead to fatigue, decreased attention, and potential safety risks. Kinfor truck accessories such as ergonomic seat cushions, lumbar supports, and cabin organizers provide a more comfortable and organized driving environment, which contributes to alertness and wellbeing.
Additional comfort accessories, including climate control enhancements, sunshades, and noise-reducing cabin elements, help maintain optimal conditions inside the truck, allowing drivers to focus on the road even during long and challenging routes.
Safety is a primary concern for long-haul operations. Kinfor truck accessories enhance both active and passive safety systems. Products such as high-visibility mirrors, LED lighting kits, and sensor-based assistance devices help drivers detect hazards early, reducing the likelihood of accidents on highways and challenging terrain.
In addition, durable protective gear, including mud flaps, reinforced bumpers, and wheel guards, safeguards the truck from damage caused by road debris or extreme weather conditions, extending vehicle lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Efficiency is key to profitability in long-haul trucking. Kinfor accessories contribute to streamlined operations by improving cargo management, fuel efficiency, and vehicle handling. Roof racks, cargo tie-downs, and aerodynamic enhancements reduce drag, optimizing fuel consumption over long distances.
Integrated storage solutions and easy-access tool compartments allow drivers to maintain organized cargo and equipment, reducing downtime during loading and unloading. The combination of practical design and durable construction ensures that these accessories remain functional over extended periods.
Long-haul trucks face constant exposure to vibration, extreme temperatures, and road debris. Kinfor truck accessories are engineered using high-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes to withstand these conditions. Components such as reinforced floor mats, heavy-duty bumpers, and protective guards ensure that trucks remain operational and in optimal condition over extended service periods.
Durability reduces the frequency of replacements and maintenance, lowering overall operating costs for fleet managers. By combining strength and reliability, Kinfor accessories support the demands of trucks that cover thousands of miles regularly.
Every trucking operation has unique requirements, depending on cargo type, route conditions, and driver preferences. Kinfor offers customizable accessories that allow fleet managers to tailor trucks to specific operational demands. From adjustable lighting systems to modular storage solutions, the ability to customize enhances both comfort and functionality.
Customization also supports compliance with regional safety regulations and industry standards, ensuring that trucks meet legal requirements while optimizing driver experience and cargo management.
| Feature | Standard Accessories | Kinfor Premium Accessories |
| Durability | Moderate | High-strength materials |
| Comfort | Basic | Ergonomic and adjustable |
| Efficiency Impact | Limited | Optimized for productivity |
Sustainable trucking relies on minimizing waste and maximizing fuel efficiency. Kinfor accessories, from aerodynamic enhancements to durable cargo systems, help reduce environmental impact by improving fuel economy and decreasing wear-related replacements. Long-lasting, high-quality components also reduce material waste and support greener operational practices.
Kinfor truck accessories combine durability, comfort, safety, and efficiency, making them essential for long-haul trucking operations. Their thoughtful design, high-quality materials, and customizable options allow fleet managers and drivers to optimize performance, reduce maintenance issues, and enhance operational reliability.
In the demanding environment of long-distance trucking, investing in reliable accessories is not optional—it is a strategic choice that impacts driver wellbeing, vehicle longevity, and overall productivity. Kinfor accessories meet these demands, supporting modern trucking operations with practical, high-performance solutions.

 How Can Kinfor Accessories Be Integrated with Smart Truck Systems?
How Can Kinfor Accessories Be Integrated with Smart Truck Systems?

Jan 16, 2026
Kinfor truck accessories encompass a wide range of aftermarket solutions designed to enhance truck performance, safety, and driver convenience. From lighting systems and cargo management solutions to protective guards and digital monitoring devices, Kinfor accessories are engineered for both commercial and personal trucks.
With the rise of smart truck systems that integrate telematics, GPS tracking, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and fleet management software, Kinfor accessories are increasingly being designed to interface seamlessly with these digital technologies, enabling optimized performance and greater operational efficiency.
Modern smart trucks rely on telematics to monitor vehicle performance, driver behavior, and maintenance schedules. Kinfor accessories, such as tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), cargo sensors, and auxiliary lighting, can be integrated with telematics platforms to provide real-time data to fleet managers and drivers.
For instance, TPMS sensors installed through Kinfor kits can transmit tire pressure and temperature data directly to the truck’s onboard system, alerting drivers to potential issues before they become critical. Similarly, digital cargo sensors can monitor weight distribution and load stability, feeding information into smart fleet software for enhanced safety.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) utilize cameras, radar, and sensors to support braking, lane-keeping, and collision avoidance. Kinfor accessories, such as custom-mounted cameras, radar shields, and enhanced mirrors, can be calibrated to work with ADAS, ensuring that the additional equipment does not interfere with sensor functionality.
Proper integration ensures that ADAS features like adaptive cruise control, automatic emergency braking, and blind-spot detection continue to function optimally, even when additional aftermarket components are installed. This allows drivers to maintain safety standards while customizing their vehicles.
Lighting is a critical component of smart truck systems, particularly for night driving and adverse weather conditions. Kinfor LED light bars, signal lights, and auxiliary lamps can be connected to a truck’s smart lighting control modules, allowing automated activation, dimming, or synchronized signaling with other systems.
Integration with smart truck systems improves visibility, reduces driver fatigue, and enhances communication with other vehicles. For fleet operators, connected lighting systems can also log usage data, helping optimize maintenance schedules and energy consumption.
Kinfor offers cargo racks, bed extenders, and load sensors that can be integrated with smart truck systems. Digital load sensors provide real-time monitoring of cargo weight and distribution, alerting drivers and fleet managers if adjustments are required.
Connected cargo management accessories improve operational efficiency by preventing overloading, optimizing fuel consumption, and ensuring compliance with transportation regulations. In commercial fleets, integration reduces risks of cargo damage and supports route planning based on vehicle load.
Kinfor accessories can enhance performance monitoring when integrated with telematics systems. Fuel efficiency sensors, engine diagnostics modules, and tire monitoring devices feed critical information to smart dashboards and fleet management platforms.
Real-time data from Kinfor-installed accessories allows operators to detect potential issues early, schedule predictive maintenance, and reduce downtime. This integration improves overall fleet efficiency while extending vehicle lifespan and reducing operational costs.
Many Kinfor accessories now feature wireless connectivity options, including Bluetooth and Wi-Fi modules. These allow sensors, cameras, and lighting devices to communicate with mobile apps, tablets, and onboard smart displays.
Through wireless integration, drivers can monitor tire pressure, lighting status, or cargo weight from a central interface. Fleet managers can also remotely access vehicle data, receive alerts, and manage multiple trucks efficiently, creating a seamless connection between hardware and software.
Integrating Kinfor accessories with smart truck systems requires careful attention to maintenance and safety protocols. All sensors, wiring, and mounts should be regularly inspected to ensure proper functionality and prevent interference with the truck’s primary systems.
Training drivers to understand data outputs from integrated accessories, such as load alerts or tire warnings, helps prevent accidents and ensures that the benefits of smart integration are fully realized. Proper installation, calibration, and regular software updates are also essential to maintain reliable system performance.
| Accessory | Integration Capability | Operational Benefits |
| TPMS Sensors | Teaches telematics systems tire data | Enhanced tire safety, reduced downtime |
| LED Light Bars | Smart lighting control modules | Improved visibility, automated activation |
| Cargo Sensors | Integrates with load management software | Optimized load distribution, operational safety |
| Wireless Cameras | Smart ADAS and mobile apps | Enhanced blind-spot monitoring, driver convenience |
Integrating Kinfor truck accessories with smart truck systems enhances operational efficiency, safety, and driver convenience. By ensuring proper installation, calibration, and maintenance, these accessories become fully compatible with digital systems, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized performance.
The combination of durable hardware and intelligent software creates a connected ecosystem where trucks operate more efficiently, safely, and sustainably. With continued innovation in Kinfor accessories and smart truck technologies, fleet operators and individual drivers can benefit from greater control, visibility, and operational effectiveness.
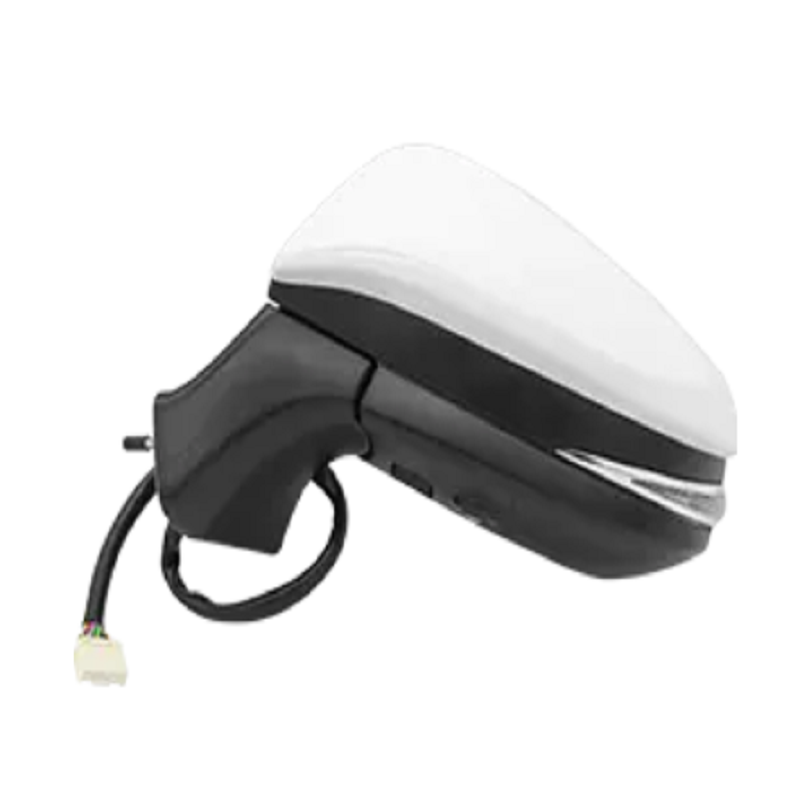
 What is the function of an automatic side mirror?
What is the function of an automatic side mirror?

Jan 06, 2026
Automatic side mirrors, also known as power side mirrors or auto-folding mirrors, are advanced components of modern vehicles that enhance safety and convenience. Unlike manual mirrors, these mirrors can adjust, fold, and react to driving conditions automatically, reducing driver effort and minimizing blind spots.
The primary functions of an automatic side mirror go beyond simple rearward visibility. They include:
Automatic side mirrors can adjust their angle based on driver settings or vehicle memory profiles. This feature allows multiple drivers to use the same car without manually reconfiguring the mirrors. Some advanced systems even adjust the mirror angle based on vehicle speed, ensuring optimal rearward visibility while reducing blind spots.
Power folding mirrors automatically fold inward when the vehicle is parked or when triggered remotely. This reduces the risk of damage from passing vehicles or pedestrians. In congested urban areas, this feature can prevent costly repairs caused by collisions with stationary objects.
Many automatic mirrors include integrated heating elements that remove frost, ice, and fog. Heated mirrors improve visibility in cold or humid conditions, reducing the need for drivers to manually clear obstructions and improving overall driving safety.
Modern automatic side mirrors are increasingly integrated with electronic safety systems to prevent accidents and enhance driver awareness.
Sensors installed within automatic side mirrors can detect vehicles in adjacent lanes. When a car enters the blind spot, the mirror provides visual or audible alerts, allowing the driver to make safer lane changes.
Some automatic mirrors feature integrated turn signal lights, improving vehicle visibility to other drivers. These signals reduce the likelihood of collisions when turning or changing lanes, particularly in low-visibility conditions.
Memory recall allows mirrors to return to preset positions automatically when different drivers use the car. This feature ensures each driver has optimal visibility immediately, reducing time spent adjusting mirrors manually.
Automatic side mirrors provide practical advantages that improve both safety and convenience for drivers.
Automatic adjustment, folding, and heating functions save drivers time. In busy environments or extreme weather conditions, these features allow for quick preparation before driving without manual intervention.
By reducing physical damage risks through power folding and alert systems, automatic mirrors help maintain vehicle aesthetics and functionality. This lowers repair costs and preserves resale value over time.
Automatic side mirrors contribute to safer driving by minimizing blind spots, improving visibility in adverse weather, and integrating with safety sensors. These features collectively reduce the likelihood of accidents during lane changes, parking, and urban driving.
Automatic side mirrors rely on several mechanical and electronic components to function effectively.
High-precision motors and actuators adjust the mirror angle and folding position. These components are engineered for durability and smooth operation, even under frequent use.
Proximity sensors, temperature sensors, and blind spot detectors provide real-time data to the mirror’s control unit. These sensors enable functions like collision avoidance alerts, automatic heating, and smart folding.
Integrated electronic control modules manage all automated functions of the mirror. They process inputs from sensors, driver settings, and vehicle systems to optimize performance and ensure safety.
The table below highlights key differences between manual and automatic side mirrors, emphasizing why automatic mirrors are increasingly standard in modern vehicles:
| Feature | Manual Mirror | Automatic Mirror |
|---|---|---|
| Adjustment | Manual | Automatic, memory recall |
| Folding | Manual | Power folding |
| Heating | Optional or not available | Integrated heating for frost removal |
| Safety Integration | Limited | Blind spot detection, turn signal integration |
| Convenience | Low | High |
Automatic side mirrors are more than just a convenience feature; they significantly enhance vehicle safety, driver comfort, and operational efficiency. Through automatic adjustment, power folding, heating, and integration with safety systems, these mirrors address blind spots, reduce accidents, and save driver effort. As automotive technology continues to evolve, automatic side mirrors will remain a key element in vehicle design and safety standards.

 Are Kinfor Truck Accessories Compatible with Telematics and Fleet Management Systems?
Are Kinfor Truck Accessories Compatible with Telematics and Fleet Management Systems?

Jan 04, 2026
Kinfor truck accessories are designed to enhance vehicle functionality, safety, and efficiency. In modern logistics and fleet operations, integrating these accessories with telematics and fleet management systems has become increasingly important. Compatibility ensures that fleet managers can monitor truck performance, driver behavior, and maintenance needs in real time while optimizing operational efficiency across large fleets.
Kinfor offers a wide range of truck accessories, including safety enhancements, cargo management solutions, driver comfort features, and electronic monitoring devices. Accessories such as tire pressure monitoring systems, GPS trackers, dashboard cameras, and advanced lighting systems are commonly used in modern fleets. These components are engineered to be compatible with various truck models while providing reliable performance under heavy-duty conditions.
The adoption of Kinfor accessories in large fleets allows for consistent standardization, easier maintenance, and improved driver satisfaction. However, their integration with digital fleet management platforms requires careful consideration of communication protocols, power requirements, and software interoperability.
Telematics systems enable fleet operators to collect, analyze, and act upon real-time data from vehicles. Key functionalities include GPS tracking, fuel consumption monitoring, engine diagnostics, driver behavior analysis, and predictive maintenance alerts. Fleet management systems often combine telematics data with scheduling, routing, and reporting tools, allowing operators to make data-driven decisions.
For truck accessories to integrate effectively, they must be compatible with standard telematics protocols such as CAN bus, OBD-II, J1939, and wireless connectivity options like Bluetooth or cellular networks. Ensuring seamless communication between Kinfor devices and fleet platforms is critical to avoid data gaps and ensure accurate reporting.
Many Kinfor accessories are designed with digital connectivity in mind. For example, GPS tracking modules can feed location and speed data directly into fleet management dashboards, while tire pressure monitoring systems alert managers to abnormal conditions in real time. Dashboard cameras and electronic logging devices can also interface with telematics software to enhance visibility and compliance.
Manufacturers provide firmware updates and API support to ensure that these devices remain compatible with popular fleet management systems. Proper installation, calibration, and configuration are necessary to ensure accurate data flow and reduce errors caused by signal interference or mismatched protocols.
Integrating Kinfor accessories with fleet management systems offers multiple benefits. First, it enhances safety by providing early warnings about mechanical issues, tire pressure anomalies, or lighting failures. Second, it improves operational efficiency by allowing real-time route optimization and vehicle monitoring. Third, it supports predictive maintenance strategies, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Additionally, integration enables detailed driver performance analysis. Telemetry data from Kinfor-installed devices can identify harsh braking, excessive idling, or speeding, allowing fleet managers to implement training programs and reward safe driving practices.
Despite the benefits, integrating truck accessories with telematics platforms presents challenges. Different vehicles and accessory models may use varying communication standards, which can cause compatibility issues. Software updates or hardware mismatches can disrupt data transmission, affecting monitoring accuracy.
To address these challenges, manufacturers and fleet operators work closely to standardize interfaces, employ middleware solutions, and provide training for installation and troubleshooting. Regular firmware updates, API documentation, and support services are crucial to maintaining long-term compatibility and reliable system performance.
| Feature | Without Integration | With Kinfor Integration |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Limited or manual checks | Immediate alerts from accessories |
| Safety Alerts | Reactive only | Proactive notifications for issues |
| Operational Efficiency | Dependent on manual logs | Optimized routing and fuel management |
| Maintenance | Scheduled by time only | Predictive and condition-based maintenance |
| Driver Performance | Limited oversight | Data-driven performance evaluation |
Kinfor truck accessories are increasingly compatible with telematics and fleet management systems, providing fleet operators with actionable data, improved safety, and enhanced efficiency. Through careful design, standardized communication protocols, and ongoing support, these accessories integrate seamlessly into modern fleet operations. Proper integration ensures that fleet managers can monitor vehicle health, optimize performance, and make informed decisions to reduce costs, increase productivity, and enhance driver and cargo safety.
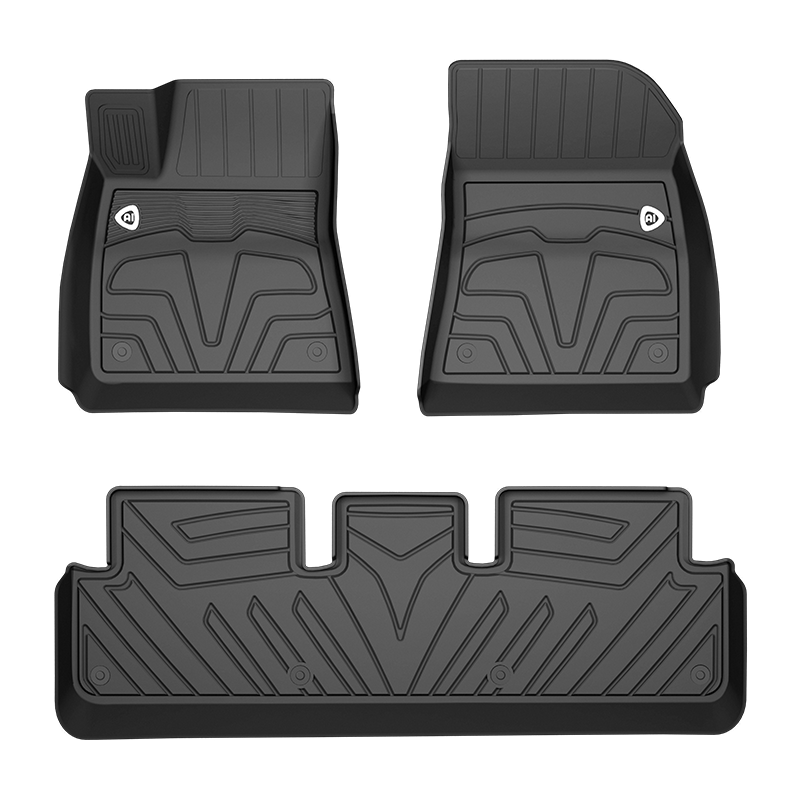
 How Do Car Floor Mats Improve Driving Comfort and Safety?
How Do Car Floor Mats Improve Driving Comfort and Safety?

Dec 24, 2025
Car floor mats are often viewed as simple interior accessories, but their impact on driving comfort and safety is far more significant than many drivers realize. Positioned directly beneath the driver and passengers, floor mats interact constantly with footwear, pedals, and cabin surfaces. Their design, material, and fit can influence posture, foot stability, cabin cleanliness, and overall driving confidence.
In modern vehicles, where comfort and safety standards continue to rise, car floor mats are engineered to serve functional purposes beyond aesthetics. From reducing driver fatigue to preventing pedal interference, they play a quiet yet essential role in everyday driving conditions.
Comfort during driving is closely tied to how naturally and securely a driver can position their feet. High-quality car floor mats are designed to provide a stable, cushioned surface that reduces strain during long periods behind the wheel.
Many premium car floor mats incorporate layered materials such as rubber backing combined with textile or foam layers. These layers absorb vibrations from the road, reducing the amount of shock transferred through the vehicle floor to the driver’s legs and feet. Over time, this cushioning effect can noticeably reduce fatigue, especially during long-distance or stop-and-go driving.
A well-fitted mat contours to the vehicle’s footwell, allowing drivers to rest their feet naturally without slipping. This consistent positioning supports better posture and reduces unnecessary muscle tension, contributing to a more relaxed driving experience.
Safety begins with control, and car floor mats directly affect how securely a driver can operate the pedals. Poorly designed or ill-fitting mats can slide, bunch up, or interfere with pedal movement, creating serious safety risks.
Modern car floor mats often feature anti-slip backing materials or factory-compatible anchoring points. These systems keep the mat firmly in place, preventing unexpected movement underfoot. Stable mats ensure consistent pedal engagement and reduce the risk of delayed braking or acceleration.
A clean driving environment contributes directly to comfort and indirectly to safety. Dirt, water, mud, and debris brought in on shoes can accumulate on the vehicle floor, creating slippery surfaces and unpleasant odors. Car floor mats act as the first line of defense against these elements.
All-weather car floor mats are designed with raised edges and textured surfaces that trap liquids and debris. By containing moisture, these mats prevent water from spreading across the cabin floor, reducing slip hazards and protecting underlying carpet materials.
Removable mats simplify interior maintenance. Instead of deep-cleaning fixed carpets, drivers can quickly remove and wash mats, keeping the cabin fresh and hygienic. A cleaner interior enhances comfort and reduces distractions caused by odors or clutter.
Worn or damaged vehicle flooring can negatively affect both comfort and resale value. Car floor mats shield original carpets from abrasion, stains, and long-term wear caused by constant foot traffic.
| Protection Feature | Comfort and Safety Benefit |
| Wear Resistance | Maintains even floor surface |
| Stain Prevention | Keeps cabin visually clean |
| Moisture Barrier | Prevents odor and mold buildup |
By preserving the original flooring, mats help maintain a consistent and comfortable footwell surface throughout the vehicle’s lifespan.
Different car floor mat materials offer varying levels of comfort and safety. Choosing the right material depends on driving habits, climate, and personal preferences.
Rubber mats excel in wet or muddy conditions. Their textured surfaces enhance grip, while their waterproof nature keeps the footwell dry. These mats are particularly effective in regions with frequent rain or snow.
Carpeted mats provide a softer feel underfoot and contribute to a quieter, more refined cabin environment. Hybrid designs combine carpet comfort with rubber backing, offering a balance between luxury and practicality.
Discomfort and instability can subtly distract drivers over time. Slipping feet, uneven surfaces, or damp flooring can draw attention away from the road. Car floor mats help eliminate these minor but cumulative distractions.
By providing a stable, comfortable base for foot movement, mats allow drivers to focus fully on steering, traffic conditions, and situational awareness. This improved focus contributes directly to safer driving outcomes.
Custom-fit car floor mats are designed to match specific vehicle models, ensuring full coverage without excess material. This precise fit enhances both comfort and safety by eliminating loose edges or folds.
Custom-fit mats are particularly valuable for drivers who prioritize predictable pedal operation and a refined interior driving environment.
Car floor mats may appear to be a minor detail, but their contribution to driving comfort and safety is substantial. From improving foot stability and pedal control to maintaining cleanliness and reducing fatigue, they influence the driving experience in practical and measurable ways.
As vehicles become more refined and drivers spend more time on the road, the role of well-designed car floor mats continues to grow. By choosing the right mats, drivers can enhance both everyday comfort and overall safety, making each journey smoother, cleaner, and more controlled.
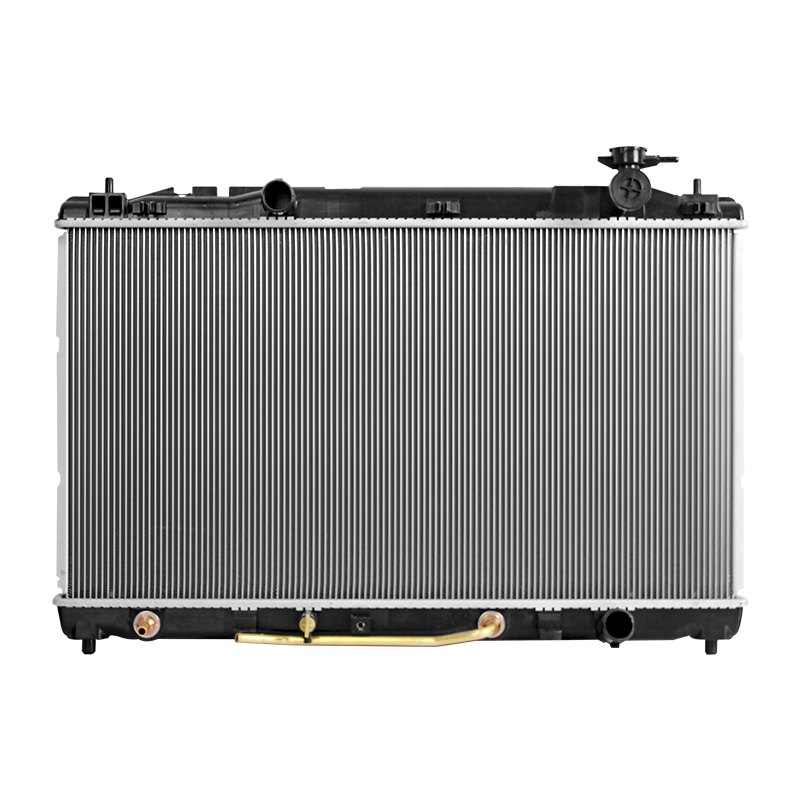
 Comprehensive guide on HVAC auto radiators
Comprehensive guide on HVAC auto radiators

Dec 19, 2025
HVAC auto radiators are a critical component in automotive heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. They are responsible for regulating the temperature of the engine coolant and ensuring that the vehicle maintains optimal operating conditions. By transferring heat from the engine coolant to the air, HVAC auto radiators prevent engine overheating and contribute to overall vehicle performance.
Modern HVAC systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with the radiator, allowing precise control over cabin temperature and engine efficiency. A properly functioning radiator ensures both engine longevity and passenger comfort, making it a key element in automotive maintenance.
Auto radiators come in various types, each designed for specific vehicle requirements. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right radiator for optimal performance.
Copper and brass radiators are traditional types known for their excellent thermal conductivity. These radiators are durable and easy to repair, making them suitable for older vehicles. They are often preferred in heavy-duty applications where reliability is essential.
Aluminum radiators are lightweight and provide superior heat dissipation. They are commonly used in modern vehicles to improve fuel efficiency. Aluminum construction allows for compact designs without compromising cooling performance. These radiators are often paired with plastic tanks to reduce weight further.
Plastic tank radiators combine aluminum cores with plastic tanks. They are cost-effective and lightweight but may be less durable than full-metal radiators. They are popular in passenger vehicles due to their balance of performance and affordability.
Understanding the components of an HVAC auto radiator is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a specific role in the cooling process.
The radiator core consists of tubes and fins that facilitate heat exchange. Coolant flows through the tubes while air passes over the fins, allowing heat to dissipate efficiently.
Inlet and outlet tanks direct coolant into and out of the radiator core. Proper sealing is essential to prevent leaks and maintain system pressure.
Cooling fans assist airflow through the radiator, especially when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly. They ensure consistent cooling under varying operating conditions.
Regular maintenance of HVAC auto radiators ensures longevity and prevents costly repairs. Here are practical tips for keeping radiators in optimal condition.
HVAC auto radiators can experience several issues over time. Early detection and troubleshooting can prevent severe engine damage.
Leaks often occur at joints, tanks, or hoses due to corrosion or wear. Corrosion can block coolant flow, reducing efficiency and causing overheating. Regular inspection and timely replacement of damaged parts are crucial.
Sediment buildup in radiator cores reduces heat transfer efficiency. Flushing the system at recommended intervals removes debris and maintains optimal cooling performance.
Malfunctioning fans or thermostats can disrupt coolant flow and airflow, leading to temperature spikes. Regular testing and replacement of these components ensure smooth operation.
Proper installation of HVAC auto radiators is critical for performance and safety. Following manufacturer guidelines minimizes potential problems and ensures efficient cooling.
Performance enthusiasts often upgrade HVAC auto radiators to improve cooling capacity and engine efficiency. Consider the following options:
| Upgrade Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| High-Performance Aluminum Core | Improved heat dissipation and reduced weight |
| Electric Cooling Fans | Enhanced airflow at low speeds and idle |
| Larger Radiator Tanks | Increased coolant capacity for heavy-duty usage |
HVAC auto radiators play a vital role in automotive performance and comfort. Choosing the right type, performing regular maintenance, and addressing issues promptly can significantly extend the life of both the radiator and the engine. Whether for standard use or performance upgrades, understanding radiator function and care ensures optimal vehicle efficiency and reliability.

 Automotive OEMs Invest in High-Tech Side Mirrors for Next-Gen Vehicles.
Automotive OEMs Invest in High-Tech Side Mirrors for Next-Gen Vehicles.

Dec 12, 2025
Auto side mirrors, once simple reflective surfaces, have evolved into high-tech components critical to vehicle safety, efficiency, and driver assistance. Modern side mirrors integrate cameras, sensors, lighting, and aerodynamic designs to improve visibility, reduce blind spots, and enhance fuel efficiency. Automotive OEMs are increasingly investing in advanced side mirror technologies to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demand for safety and convenience. This article explores the latest innovations, practical applications, and future trends in auto side mirrors for next-generation vehicles.
High-tech side mirrors now play a pivotal role in active safety systems. Features such as blind-spot detection, lane departure warnings, and integrated turn signals provide real-time alerts to drivers, preventing accidents and improving road safety. Side mirrors equipped with cameras and radar sensors feed data to advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), enhancing vehicle awareness and responsiveness in complex traffic situations.
Cameras embedded in auto side mirrors improve visibility and support advanced functionalities. Replacing traditional mirrors with digital displays, sometimes referred to as “camera-monitor systems,” offers a wider field of view and better performance in low-light conditions. This technology also reduces blind spots, assists with parking, and integrates with surround-view monitoring systems for a comprehensive driver perspective.
Aerodynamic optimization of side mirrors reduces wind resistance and noise while improving vehicle fuel efficiency. Lightweight materials such as carbon fiber, aluminum, and reinforced polymers contribute to weight reduction without compromising durability. Streamlined mirror shapes and minimized protrusion enhance airflow, decreasing drag coefficients and contributing to overall vehicle efficiency.
Heated side mirrors prevent fogging and ice buildup in cold climates, ensuring consistent visibility. Adaptive mirrors automatically adjust angle and tilt based on driving conditions or reversing maneuvers, enhancing safety and convenience. Such features, once considered premium, are becoming standard in next-generation vehicles due to increasing safety expectations.
Automotive OEMs are investing heavily in high-tech side mirror development, reflecting the importance of safety, aesthetics, and regulatory compliance. Partnerships with technology providers for sensor integration, camera systems, and AI-based monitoring are increasing. The global trend toward electric and autonomous vehicles drives demand for digital side mirrors and lightweight materials to enhance efficiency and functionality.
Auto side mirrors have transformed from simple reflective devices to integrated high-tech systems crucial for vehicle safety, efficiency, and comfort. Investments by OEMs in advanced materials, sensors, cameras, and adaptive technologies are shaping next-generation vehicles with superior visibility, reduced aerodynamic drag, and enhanced driver assistance. As innovation continues, high-tech side mirrors will play a central role in automotive design and the evolution of smart, connected, and autonomous mobility.
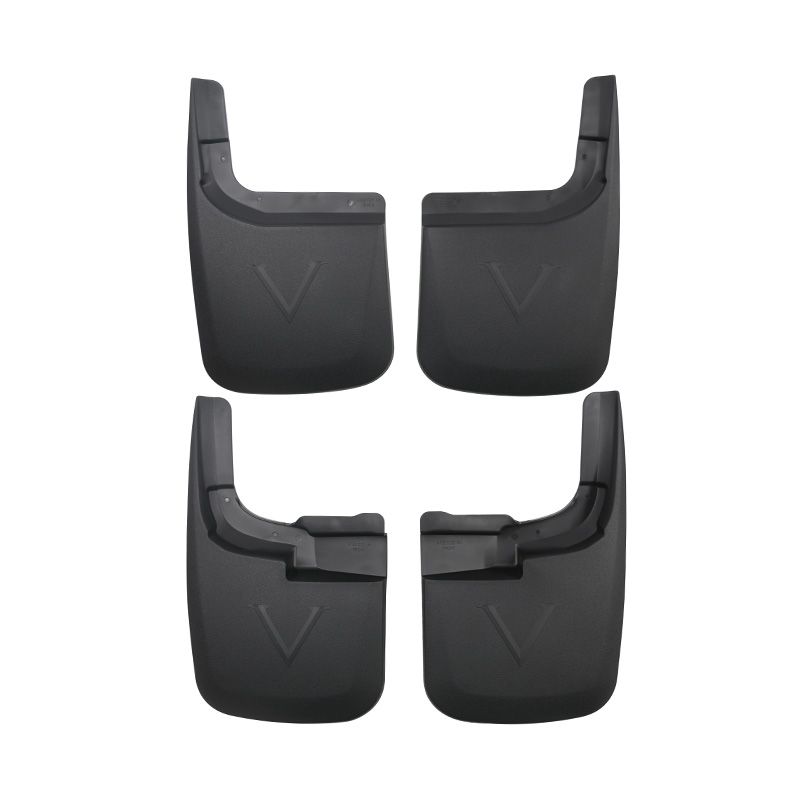 Can Mud Flaps effectively reduce road splashing and mud?
Can Mud Flaps effectively reduce road splashing and mud?

Dec 04, 2025
Mud flaps, also known as splash guards, play a vital role in controlling the debris, water, and mud kicked up by a vehicle’s rotating tires. While simple in appearance, their function is grounded in basic physics and practical engineering. Understanding how mud flaps reduce splashing helps drivers make better decisions about installation, materials, and performance expectations.
When tires rotate at high speeds, they pick up moisture, mud, rocks, and debris from the road surface. Centrifugal force throws these elements outward and upward, creating a spray pattern that affects vehicles behind and around the car. Mud flaps interrupt this trajectory by acting as a flexible physical barrier, absorbing the force of incoming debris and redirecting it downward toward the ground.
The spray from tires is influenced by tread design, road conditions, driving speed, and moisture levels. Without an external barrier, tire spray tends to disperse in a wide fan-shaped pattern. Mud flaps narrow this spread, helping maintain clearer visibility for trailing drivers and reducing the accumulation of dirt along the sides of the vehicle.
High-quality mud flaps are designed to minimize splash by directing debris downward rather than outward. Their flexible material helps absorb impact energy and slow the debris before releasing it at a lower angle. This improves safety particularly in high-speed highway travel or wet environments where spray can significantly impair visibility.
Different types of mud flaps offer varying degrees of splash protection depending on size, material, and intended vehicle use. Selecting the right one can greatly enhance performance in harsh weather or off-road environments.
| Material | Characteristics | Effectiveness |
| Rubber | Flexible, durable, excellent impact absorption | High |
| Plastic | Lightweight, rigid, affordable | Moderate |
| Polyurethane | High flexibility, resistant to cracking | High |
| Metal-Reinforced | Suitable for heavy-duty trucks and towing | Very High |
Full-width mud flaps are commonly used on commercial trucks and trailers, extending across the entire vehicle width for maximum splash control. Individual flaps behind each wheel are typical for cars, SUVs, and pickup trucks. Full-width options offer superior protection but are unnecessary for most passenger vehicles unless towing or driving in heavy mud conditions.
Beyond reducing road splashing, mud flaps offer several practical benefits that improve driving comfort and prolong vehicle longevity. Their protective function expands beyond mud, helping limit wear and damage from road elements.
Mud flaps significantly reduce the amount of dirt and grime thrown onto the lower panels of the vehicle. This minimizes the frequency of washing and helps preserve paint quality. In winter climates, they also help reduce salt splash, which can accelerate corrosion.
Spray reduction is especially important for vehicles traveling at high speeds or in rainy conditions. By limiting the spray that obscures visibility for drivers behind the vehicle, mud flaps contribute to safer driving conditions. For commercial fleets, splash reduction can drastically improve road safety metrics.
Tires often pick up small rocks that can chip paint or crack windshields of trailing vehicles. Properly installed mud flaps deflect these rocks downward before they gain enough velocity to cause damage. For off-road vehicles, reinforced mud flaps are essential to avoid damage caused by gravel and debris.
To ensure mud flaps perform effectively, proper installation, sizing, and maintenance are crucial. Incorrect positioning can reduce their ability to control splash or cause them to wear prematurely.
Mud flaps should be installed close enough to the ground to block debris but high enough to avoid dragging. Typically, a ground clearance of 3–5 inches is recommended for passenger vehicles, while commercial trucks may require specific measurements to meet local regulations.
Wider and longer flaps provide better splash control, especially for trucks with large tires. However, excessively large flaps can catch wind, increasing drag or causing noise. Manufacturers often design vehicle-specific mud flaps to match wheel arch geometry for optimized performance.
Over time, mud flaps may crack, warp, or loosen due to weather exposure and road impact. Regular inspection ensures they remain effective and safe. Drivers should check for debris buildup behind the flap and ensure mounting hardware remains tight to prevent detachment.
Mud flaps are highly effective at reducing road splashing and minimizing the amount of mud, water, and debris thrown by tires. Their performance depends on material quality, proper installation, and suitability for the vehicle’s specific driving conditions. For anyone driving in wet, muddy, or gravel-filled environments, mud flaps provide a practical and reliable layer of protection that improves vehicle safety, cleanliness, and longevity.
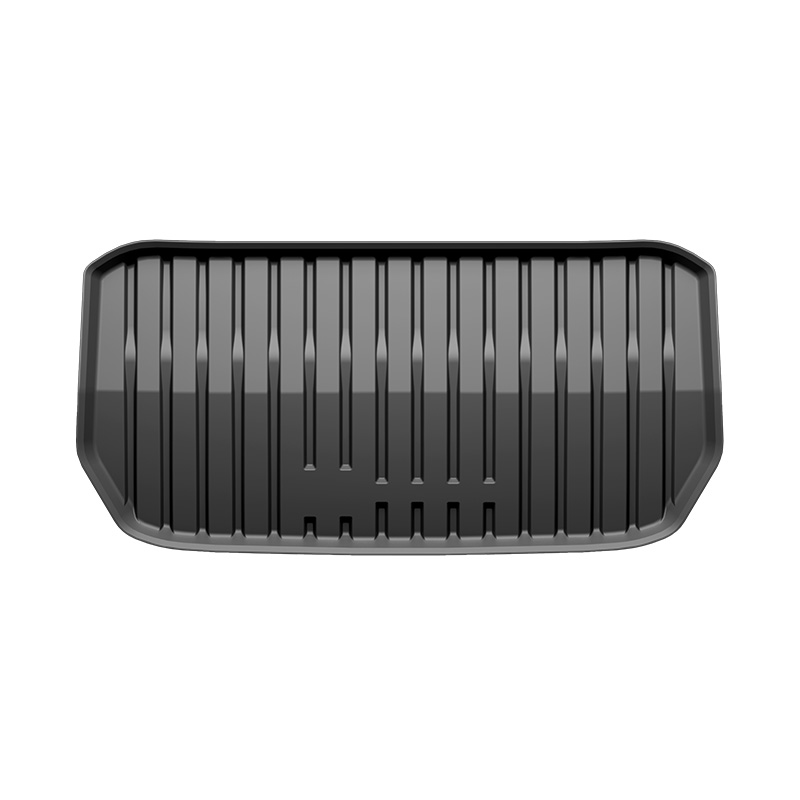
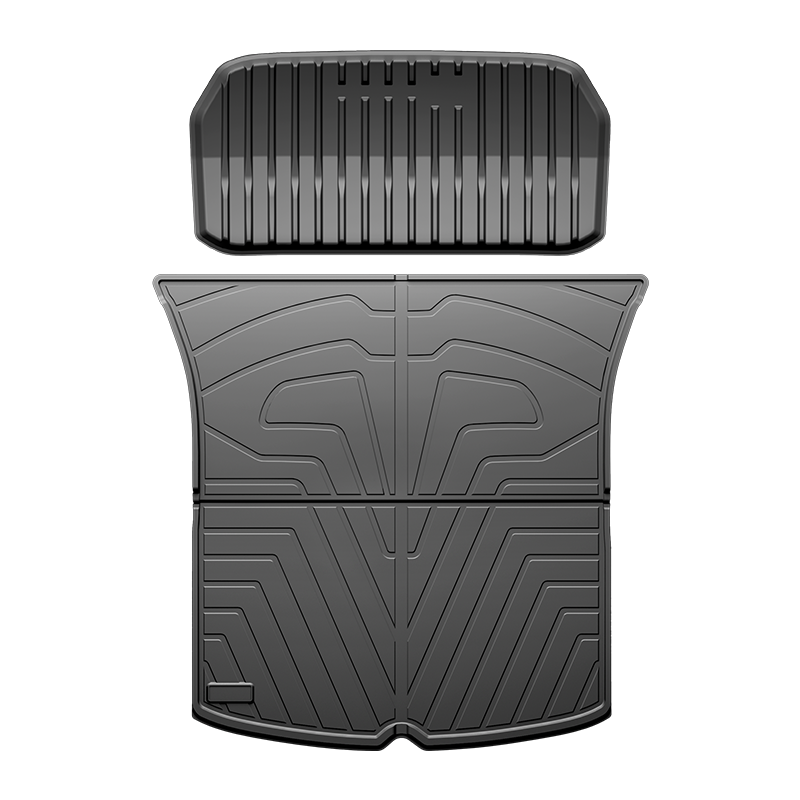
 How waterproof is the Car Trunk Mat?
How waterproof is the Car Trunk Mat?

Nov 24, 2025
A car trunk mat is designed to shield your vehicle’s cargo area from dirt, spills, and moisture. The waterproof capability of a trunk mat ensures that liquid spills do not seep into the underlying carpet, preventing damage and unpleasant odors. Modern mats are constructed from high-quality materials like thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), rubber, or PVC, which provide excellent water resistance.
The waterproof performance of a car trunk mat depends largely on its material. Here are the commonly used materials:
Beyond materials, the design of a car trunk mat plays a critical role in waterproof performance. Key features include:
Manufacturers perform various tests to ensure mats meet waterproof standards. These tests include:
Even the most waterproof mat can lose efficiency if neglected. Recommended maintenance includes:
Not all trunk mats provide the same level of waterproof protection. Here is a quick comparison:
| Material | Waterproof Rating | Durability |
| Rubber | Excellent | High |
| PVC | Good | Medium |
| TPE | Excellent | High |
Investing in a high-quality waterproof trunk mat provides multiple advantages:
A waterproof car trunk mat is an essential accessory for protecting your vehicle’s interior from liquid damage. By selecting mats made of high-quality materials, featuring thoughtful design elements, and following proper maintenance, you can ensure reliable protection against spills and moisture. Choosing the right mat enhances both the functionality and longevity of your car’s trunk space.

 How useful is an Auto Side Mirror in winter?
How useful is an Auto Side Mirror in winter?

Nov 19, 2025
Auto side mirrors are essential safety features that allow drivers to monitor traffic and obstacles around the vehicle. In winter, adverse weather conditions such as snow, ice, and fog can severely limit visibility, making side mirrors even more critical. Ensuring that side mirrors function properly and remain clear of frost and condensation can prevent accidents and improve overall driving safety.
Modern vehicles often include heated or anti-fog side mirrors that mitigate winter challenges. Understanding how these features work and why they are valuable in cold weather can help drivers make informed decisions about vehicle safety and maintenance.
Winter conditions pose several challenges for auto side mirrors. Ice accumulation on the mirror surface can obscure the driver’s view, while fogging due to temperature differences between the interior and exterior can reduce visibility. Snow buildup and road spray from other vehicles further compromise the mirror’s effectiveness.
Poorly maintained or manual side mirrors can freeze, making them difficult to adjust or even damage the mirror housing. In addition, cold weather can affect electronic components in powered mirrors, potentially impairing features such as auto-folding or memory settings. Drivers must understand these risks to maintain safe driving practices in winter.
Heated side mirrors are equipped with electrical heating elements that warm the mirror surface to melt ice and prevent condensation. This feature is especially useful during frosty mornings or during active snowfall. By maintaining a clear mirror surface, heated mirrors improve the driver’s ability to monitor traffic, lane positions, and obstacles.
Heated mirrors are typically integrated with the vehicle’s defrost system, activating automatically when the rear window defrost is turned on. This ensures the mirrors remain clear without requiring manual intervention, enhancing convenience and safety.
Electric or power side mirrors allow drivers to adjust mirror angles from inside the vehicle. This feature is particularly useful in winter when manual adjustment can be difficult due to frozen or stiff mechanisms. Power mirrors often include memory functions that return the mirror to pre-set positions, helping maintain optimal visibility without exposing the driver to cold weather for extended periods.
Auto-folding mirrors add another layer of protection, retracting to prevent damage from snow accumulation or narrow parking spaces. These features reduce the likelihood of breakage or ice-related mechanical issues.
Some modern auto side mirrors include anti-glare coatings or electrochromic technology to reduce glare from headlights and streetlights at night. In winter, shorter daylight hours and snow reflection can amplify glare, making these features highly beneficial for driver comfort and safety.
Additionally, mirrors with integrated blind spot monitoring systems provide alerts when vehicles approach from the side. This functionality is especially useful in icy or slippery conditions when changing lanes or merging can be more hazardous.
Maintaining side mirrors during winter is essential to ensure optimal performance. Key practices include:
Auto side mirrors are critical for safe driving in winter conditions. Heated and power-adjustable mirrors improve visibility, reduce the risks associated with ice and snow, and offer convenience and protection against damage. Features such as anti-glare coatings and blind spot monitoring further enhance safety during winter driving. Proper maintenance and awareness of mirror functionality ensure that drivers can navigate icy, snowy, and low-visibility conditions with confidence.

 Can Fender Flares improve a car's performance?
Can Fender Flares improve a car's performance?

Nov 14, 2025
Fender flares are an often-overlooked vehicle modification, yet they can significantly impact both the performance and aesthetic appeal of a car. Typically attached to the wheel arches, these extensions are designed to provide coverage for wider tires, protect the vehicle from debris, and enhance the overall look. While their primary function may seem cosmetic, fender flares can offer real, functional benefits that extend beyond mere appearance.
Fender flares are more than just a visual upgrade. In certain driving conditions, they can actually enhance a vehicle's performance. Here's how:
Although it may not seem obvious, fender flares can play a role in aerodynamics. When designed correctly, fender flares can help manage airflow around the vehicle, reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency. This is especially true for off-road vehicles, where flares can help direct air around the tires, preventing unwanted turbulence that could affect handling.
For vehicles equipped with larger tires, fender flares are essential. These modifications offer the clearance needed for wider wheels, which can improve handling and traction. For off-road vehicles or those used for towing, wider tires provide better grip and stability. Fender flares ensure that the larger tires do not rub against the body of the vehicle, preventing damage to both the tires and the vehicle.
By allowing for larger tires, fender flares can indirectly improve the suspension system's performance. Larger tires absorb shocks more efficiently, offering a smoother ride. Additionally, these tires are often paired with upgraded suspension systems to better handle rough terrain. Fender flares are an essential component in enabling these improvements.
While performance is one aspect, fender flares also play a crucial role in protecting the vehicle. Here's how:
Fender flares extend beyond the wheel wells, preventing dirt, rocks, and road debris from damaging the vehicle's body. This is particularly important for drivers who frequently navigate off-road conditions or rough, unpaved roads. By deflecting debris, fender flares help maintain the integrity of the vehicle's paintwork, reducing the risk of rust or scratches.
Fender flares also help reduce water splashing from the wheels, especially during rainy conditions. This is beneficial for maintaining visibility while driving and reducing the amount of mud or grime that accumulates on the vehicle’s body. This feature is particularly useful for trucks and off-road vehicles that often face challenging environmental conditions.
Beyond performance and protection, fender flares can also influence how a vehicle handles on various terrains. Their ability to accommodate larger tires can provide better traction, which enhances grip on wet or uneven surfaces. However, there are a few things to consider when choosing fender flares for performance:
Wider tires generally offer more traction, especially on off-road surfaces like gravel, mud, and sand. When paired with fender flares, these tires perform better in challenging conditions, as they maintain contact with the ground, improving stability and handling.
The material used for fender flares can affect handling, especially for off-road vehicles. Plastic, fiberglass, and polyurethane are common materials, with each offering different levels of durability, flexibility, and weight. Lighter materials may have a negligible impact on overall performance, while heavier materials can add weight to the vehicle, potentially impacting fuel efficiency or handling in extreme conditions.
Aside from their functional benefits, fender flares can dramatically change the look of a vehicle. Whether you're looking to give your vehicle an aggressive, off-road-ready appearance or simply want to enhance its overall appeal, fender flares provide an affordable and effective solution. The visual upgrade is often just as important for vehicle owners as the performance benefits.
Fender flares come in a wide variety of styles, allowing vehicle owners to personalize their cars according to their preferences. Whether you prefer the rugged, utilitarian look for off-road vehicles or a sleek, streamlined appearance for a more urban aesthetic, there's a set of fender flares to fit any style.
Fender flares can be chosen based on the size and shape of the vehicle’s wheel wells. Options range from subtle, narrow flares to more pronounced, wide extensions that provide a more aggressive look. Additionally, the design can complement the vehicle's body lines, helping the flares blend seamlessly with the overall design.
Fender flares offer a blend of performance and aesthetic benefits, but they do not provide a dramatic performance improvement on their own. When combined with larger tires and an upgraded suspension system, however, they can enhance a vehicle's handling, traction, and overall stability. They also offer crucial protection from road debris, improving the longevity and condition of the vehicle. In essence, fender flares are a practical modification that can improve both the look and function of your vehicle, especially for off-road enthusiasts or those looking to optimize their driving experience.
